What is Material Handling? Principles, Benefits & Equipment
Material handling is at the core of every warehouse operation.
More than just moving goods from one place to another, it defines how materials are received, stored, transported, and picked.
The goal is ensuring a consistent, safe, and efficient flow of products throughout the supply chain.
It’s no surprise that the global warehousing and distribution logistics market was valued at $13.5 trillion in 2023, with projections of 5% annual growth through 2032.
The rise of eCommerce and demand for fast, accurate fulfillment are accelerating the need for reliable material handling systems.
Despite the constant movement, warehouses don’t have to be chaotic or overly labor-intensive, as long as the proper systems are in place.
With an organized material handling system and specialized equipment, warehouse operators can boost productivity, streamline goods movement and reduce safety risks.
But what is material handling exactly, and what does it entail?
We’re about to find out.
In this article, we will:
- Cover all you need to know about material handling
- Explore how it’s implemented into the supply chain
- Discover the types of warehouse equipment used and the benefits of integrating them into your facility
- Share how our automated solutions fit into the materials handling puzzle to help optimize your warehouse operations
What is Material Handling?
Material handling is the movement, protection, storage, and control of materials and products throughout the entire supply chain, from manufacturing and distribution all the way to consumption and disposal.
The primary goal is to efficiently get the right material to the right place, at the right time, and in the right condition, all while minimizing costs and maximizing worker safety.
While it is a core function in warehousing and logistics, its principles are essential in virtually every industry, including manufacturing, retail, construction, and healthcare.
This process relies on a wide range of manual, semi-automated, and automated equipment.
Types of Material Handling Equipment
Material handling equipment is grouped into four main categories: storage and handling, bulk material, industrial trucks and engineered systems. Let’s take a look at each one.
1. Storage and Handling Equipment
Storage and handling equipment protects goods between stages of the supply chain, whether for short- or long-term holding, depending on your warehouse’s needs.
Storage and handling equipment includes:
- Pallet racks: Vertical structures made of steel framing with connectors and beams to store products
- Shelves, bins and drawers: Shelves, drawers and bins within shelving units store smaller materials.
- Mezzanines: Wooden, steel or fiberglass raised platforms that create additional storage
- Stacking frames: Equipment that stores and stacks numerous pallets and racks
2. Bulk Handling Material Equipment
Bulk material handling equipment stores, controls and transports loose form materials in large quantities.
Loose form materials can include liquid, food and minerals, such as stones and rocks, and metal items, such as bolts and nails.
Bulk handling equipment includes:
- Conveyor belts: Two or more belts and pulleys to transport products from one location to another
- Stackers: Equipment that loads and unloads heavy materials and places them onto stockpiles or storage for bulk materials
- Reclaimers: Reclaimers are used to pick out materials from stockpiles
- Bucket elevators: Designed for handling and lifting large amounts of bulk materials through the system
- Hoppers: Funnel-shaped equipment used to dump or pour loose form materials into containers
3. Industrial Trucks
Industrial trucks are vehicles that transport goods and materials within your warehouse and are also utilized to load or unload heavy objects.
There are several different types of industrial trucks. Some have forks or a flat surface to lift products, while others need additional equipment for lifting.
Industrial trucks can range from small, hand-operated machines to large, drivable equipment.
Industrial trucks include:
- Forklifts: Industrial trucks that raise and lower goods in short distances
- Hand trucks: Also called dollies, industrial trucks are manually pushed by hand and consist of two wheels and a small ledge to carry goods
- Pallet Trucks: Also known as pallet jacks, pallet trucks are designed to lift and move pallets
- Sideloaders: Industrial trucks that go through narrow aisles, and load and unload goods from the machine’s sides
- Order pickers: These machines safely lift operators, allowing them to access hard-to-reach materials on high shelves
4. Engineered Systems
Engineered or automated systems that incorporate warehouse technology supported by computers and robots to store and transport goods.
An automated system is generally made out of several units controlled by a management software application.
Engineered systems include:
- Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs): Sophisticated robots that navigate their environment independently, using sensors and maps to dynamically plan the best route and avoid obstacles
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS): Computer-controlled solutions that automatically store and retrieve goods from a high-density structure. Minimizing manual labor.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs): Robotic vehicles that move materials along predefined paths. They navigate using methods like magnetic tape, wires in the floor, or laser guidance and are best suited for repetitive, consistent tasks
This is where Modula comes in. At Modula, we provide the most advanced automated storage and retrieval systems to increase productivity and accuracy throughout your warehouse.
Our Vertical Lift Modules, Horizontal Carousels and Order Picking Solutions are designed to optimize space, reduce errors and speed up operations to create a seamless material handling process, from start to finish — more on this below!
GF MACHINING SOLUTIONS: Vertical Storage Units Fully Integrated with ERP and Modula WMS.
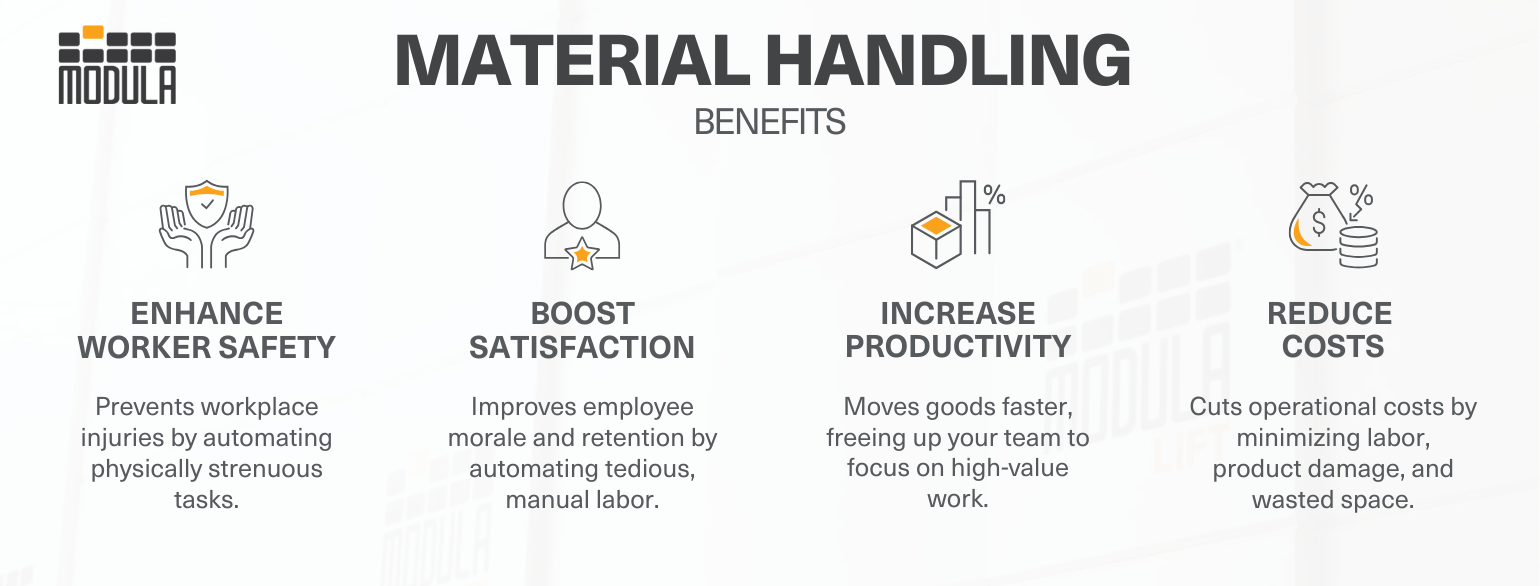
Benefits of Material Handling
An effective materials handling system maximizes storage, reduces transportation and picking time, enables real-time inventory control, cuts warehouse costs and streamlines goods flow throughout the facility. Key benefits include:
1. Prevents Workplace Accidents
The transportation and warehousing sector reported 4.5 recordable injuries per 100 full-time workers in 2023, according to the latest Employer‑Reported Workplace Injuries and Illnesses release.
Proper material handling equipment minimizes the need for employees to perform risky tasks, like manually lifting heavy items or reaching high shelves. This focus on ergonomics directly reduces strains, and other common workplace accidents.
2. Improves Employee Satisfaction
Repetitive, physically strenuous work can lead to burnout and low morale.
By automating tedious and labor-intensive tasks, you create a better work environment.
This frees employees from monotonous jobs, reduces stress, and allows them to feel more valued, which is crucial for retaining a skilled workforce.
3. Increases Productivity and Efficiency
Material handling systems automate the movement of inventory, allowing your team to stop wasting time searching for items or transporting them across the facility. This frees up skilled employees to focus on higher-value tasks like quality assurance, customer service, and process improvement, dramatically increasing overall productivity.
4. Reduces Operational Costs
With U.S. warehouse costs rising 8.3% from 2022 to 2024, profit margins are tightening.
A smart material handling system delivers a strong return on investment by:
- Cutting labor costs through automation
- Minimizing expensive product damage with controlled movements
- Maximizing your existing warehouse space to avoid costly expansions
- Increasing throughput so you can process more orders without increasing overhead
How is a Materials Handling System Implemented Throughout the Supply Chain?
From manufacturing to distribution, materials handling is key to ensure your materials and goods are safely transported from one stage of the supply chain to the next.
Here’s how materials handling is implemented in the supply chain:
- Manufacturing: Systems move raw materials to the production line and transport finished goods to storage. This includes everything from conveyor belts moving parts between assembly stations to forklifts stacking completed products.
- Transportation: At the loading dock, material handling is key for efficiently and safely loading goods onto trucks, containers, or rail cars. This ensures vehicles are loaded to capacity and sent off quickly.
- Storage & Order Fulfillment: Inside a warehouse or distribution center, goods are offloaded and put away into designated storage systems like pallet racks. When an order comes in, equipment is used to pick, pack, and sort items to prepare them for shipment.
- Distribution: In the final step, systems like forklifts and conveyor belts are used to load sorted and packed goods onto outbound trucks for delivery to retailers, wholesalers, or directly to customers.
10 Material Handling Principles to Streamline Your Operations
To operate efficiently and safely, every warehouse needs a strategy. The Material Handling Institute (MHI) established 10 principles that act as a guide for designing and managing effective material handling systems. Following these principles will help you reduce costs, improve safety, and boost overall productivity.
1. Planning: A plan should guide all material handling. Before you move a single box, define your objectives, needs, and functional specifications for every move and storage activity. The plan should answer what materials are moving, where they’re going, and how they’ll get there.
2. Standardization: Standardize your process and equipment to achieve predictable results while considering flexibility. For instance, if you have boxes of the same size, your team should anticipate future changes regarding box sizes so you can choose equipment that can efficiently transport smaller or larger boxes in the future.
3. Work: The goal of this principle is to minimize the amount of work, the distance and number of times a product is handled. Every move adds cost and risk, so eliminate unnecessary steps and combine tasks whenever possible..
4. Ergonomics: Recognize human capabilities and limitations by designing tasks and workstations that are safe, comfortable, and efficient. Ergonomic equipment and processes reduce employee fatigue, prevent injuries, and boost morale.
5. Unit load: Handle goods in the largest, most efficient unit load possible. Grouping individual items onto a single pallet, tote, or container creates a unit load. Moving one full pallet is far more efficient than moving 100 individual boxes, saving time, reducing trips, and minimizing the potential for product damage.
6. Space Utilization: Organize your warehouse to maximize your available warehouse space. You can ensure your warehouse is organized by clearing warehouse aisles of clutter, stacking inventory to utilize vertical height and grouping products in the same category.
7. System: Integrate all storage and handling activities into a single, cohesive system.
Integrate tracking tools and integrated software so you can quickly identify materials and products at every stage of the system.
8. Environment: Choose solutions that are environmentally conscious. This principle encourages using equipment that reduces energy consumption and minimizes environmental impact. It also involves planning for the reuse and recycling of packaging materials and the proper disposal of equipment at the end of its life.
9. Automation: Automate processes where it’s feasible and can provide a strong return on investment. Automation in tasks like picking, retrieval, and transport can dramatically reduce labor costs, improve accuracy, increase throughput, and enhance worker safety.
10. Life Cycle Cost: Utilize a comprehensive analysis of life cycle costs on materials handling equipment to ensure durability and sustainability. Consider different criteria, including programming, installation, setup, operation, repair and maintenance and reuse value and disposal.

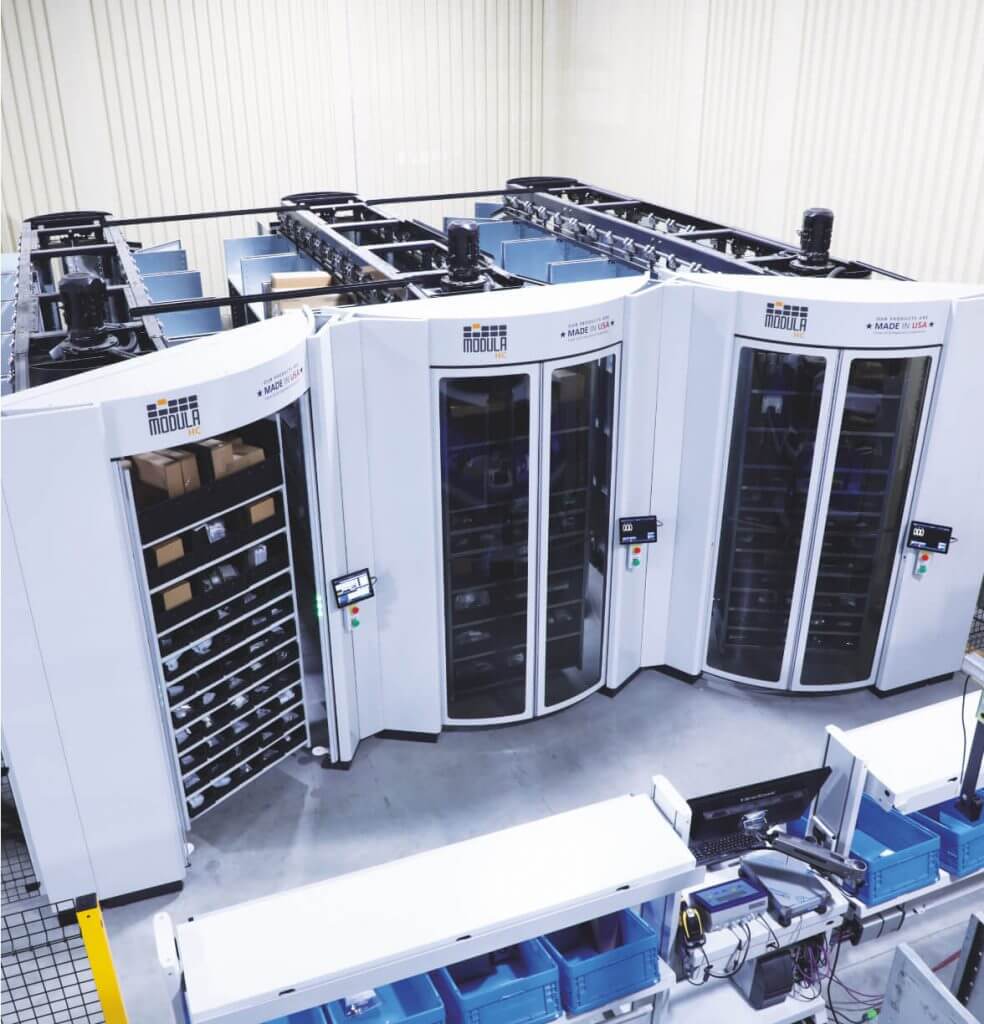
How Modula’s Solutions Contribute To A Seamless Material Handling Process
At Modula, we take material handling to the next level using the most advanced automated storage and retrieval systems.
Our automated solutions boost accuracy and productivity, improve employee safety and reduce storage space requirements.
Modula Vertical Lift Modules
Modernize your warehouse operations by going vertical with three options:
- Modula Lift is the optimal storage solution for industrial materials, spare parts and components for every industry and workplace environment
- Modula Slim is the ideal solution for warehouses with minimal floor space requiring flexible storage options
- Modula Next combines the space-saving power of vertical lift modules (VLMs) with the precision, control, and access management of industrial vending technology.
- Modula Pallet optimizes warehouse storage by stacking pallets vertically; no forklifts required.
- Modula Flexibox is capable of processing up to 180 bins per hour, Modula Flexibox delivers high-speed picking for fast-paced industries without sacrificing flexibility.
Our Vertical Lift Modules allow you to:
- Keep your employees safe by eliminating the challenges of reaching high and low areas
- Improve efficiency by retrieving the items needed from a small number of VLM stations
- Safeguard your products by storing them in an enclosed setting that only designated employees can access
- Increase productivity thanks to picking speeds of 300 lines per hour
- Lower operational cost as well as employee cost
- Anticipate requirements and offer the possibility for future growth
- Pay off the investment rapidly, with an ROI anywhere from six to 18 months
Modula Horizontal Carousels
Modula Horizontal Carousels turbocharge your warehouse operations when ceiling height is limited.
Our Horizontal Carousels allow you to:
- Facilitate quick and accurate picking operations with put-to-light systems and barcode readers
- Increase picking rates of up to 550 lines per hour for each warehouse operator
- Monitor picking operations in real-time thanks to automation
- Find and retrieve goods quickly with Modula’s digital Copilot

Modula Warehouse Management Solutions
Pair your automated storage systems with our warehouse management solutions to boost productivity, accuracy and efficiency.
Warehouse management solutions offer better control over inventory tracking, materials handling, process analysis and preventive maintenance guidance.
Our smart warehousing solutions allow you to operate in multi-order and batch modes to increase productivity without compromising your order fulfillment process for larger than usual orders.
Modula Web Analytics is a support and remote warehouse management platform that collects data from your AS/RS wherever they are in your warehouse.
With Modula Web Analytics, you can:
- Manage and monitor your warehouse operations in real-time, 24/7
- Gather your data in an easy-to-navigate online portal
Key Takeaways on Material Handling
Material handling goes beyond moving goods, it standardizes how products are transported from manufacturing to distribution, making it essential to warehouse operations
Types of material handling equipment include storage and handling equipment, bulk handling material equipment, industrial trucks and engineered systems
An effective materials handling system shortens picking and transport time, enables real-time inventory control, lowers costs and streamlines goods flow
Material Handling: FAQs
What is the primary goal of material handling?
The core objective of material handling is to enhance operational efficiency, increase productivity and ensure workplace safety, all while minimizing waste and controlling costs to support overall profitability.
What is an example of material handling?
Material handling involves the use of equipment and systems to move, store or manage goods throughout a facility.
Common examples include forklifts, conveyor belts, shelving units and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs).
How does material handling impact worker safety?
Good material handling practices help protect workers by reducing the need for heavy lifting, repetitive movements and awkward reaching.
Using automation and ergonomic equipment not only lowers the risk of injury but also makes daily tasks faster and more manageable.






