What Is Lean Warehousing? Benefits, 5S Principles & Best Practices
Whether it’s eliminating waste by removing cumbersome warehouse processes or ensuring your warehouse employees are safe, lean warehousing is the solution to several different challenges in warehouse management.
We’ll share all you need to know about lean warehousing, from benefits and principles to best practices and beyond.
Plus, we’ll introduce you to our advanced automated storage solutions and inventory management systems at Modula to help you implement a lean approach to your warehouse.
What Is Lean Warehousing?
Lean warehousing is an approach to warehouse management that eliminates warehouse processes or activities that use resources but do not create additional value, to help reduce waste and improve productivity.
This approach was initially developed in the manufacturing industry — in the automotive sector by Toyota — with a focus on reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Let’s take a manual picking process as an example. Manual picking requires your warehouse operators to use pick lists and navigate pick locations manually, which can be seen as wasteful, as it uses resources, such as time and labor, but it doesn’t add any value for your customer.
To resolve the wasted resources from manual picking, implementing the lean warehousing approach in this situation might mean taking advantage of automated picking solutions instead.
Benefits of Lean Warehousing
Lean warehousing can help you reduce waste, eliminate unnecessary processes and boost the productivity and efficiency of your warehouse operators.
Key benefits of lean warehousing include:
- Improve productivity: Lean warehousing focuses on eliminating wasteful warehouse processes, such as overproduction and excess inventory storage. By identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities, productivity is improved.
- Boost employee safety: Lean warehousing prioritizes workplace safety by utilizing warehouse automation to eliminate the need to reach high and low places, reducing both clutter and unsafe work practices.
- Increase employee morale: Lean principles promote employee involvement and empowerment. By involving your employees in continuous improvement initiatives, you can boost retention rates and allow your employees to feel valued and motivated to contribute to the success of the warehouse.
- Reduce downtime: By improving processes across your warehouse, you can reduce downtime and ensure your warehouse operations run smoothly.
- Reduce the need for more storage space: Instead of moving to a bigger facility, implementing the lean approach to your existing warehouse allows you to optimize inventory levels and reduce excess stock. This, in turn, allows you to save on premium costs associated with warehouse expansion or leasing additional storage facilities.

The 5S Principles of Lean Warehousing
The 5S principles are a fundamental part of all lean methodologies, including lean warehousing.
These principles can help you create an efficient, organized, and safe working environment when applied to every aspect of the warehouse operation — from the layout of your warehouse to how goods are picked and packed.
The 5S principles (and their Japanese counterparts) include:
1. Sort (Seiri)
The Sort principle states that each item in the warehouse should be thoroughly evaluated to ensure it is valuable. Any items that are obsolete, redundant or rarely used should be removed.
To implement the Sort principle, eliminate anything that isn’t regularly used and discard unnecessary items in your warehouse, such as unused tools and equipment.
If you have slow-moving inventory that has been sitting for a long period of time, store these items in a separate storage area to free up space in your warehouse. This makes it easier for your warehouse operators to find the items they need, enhancing efficiency.
2. Set in Order (Seiton)
The Set in Order principle states that items should be stored in specific locations based on their frequency of use, ensuring that they are accessible when needed.
To implement the Set in Order principle, organize your inventory to ensure that it is easy to find and access.
For example, you can implement the ABC analysis method to categorize goods based on their value and turnover.
Store your fast-moving items (category A) in easy-to-access areas near the dispatch area, while keeping your slow-moving items (category C) in less frequently accessed areas, such as mezzanines or in the back corner of your warehouse.
3. Shine (Seiso)
The Shine principle states that a clean and well-maintained warehouse is crucial for promoting safety and efficiency.
To implement the Shine principle:
- Establish a routine for regular cleaning and organizing activities: Make a schedule for sweeping, dusting and mopping floors, wiping down surfaces and removing debris or trash. Assign responsibilities to specific warehouse employees or hire professional cleaning services.
- Utilize shelves, racks and bins: Make sure items are stored in an organized and easily accessible manner. Implement labeling systems or barcode scanners to facilitate quick identification and retrieval of goods.
- Optimize your warehouse layout: Minimize congestion and allow for efficient movement of goods. Make sure pathways are clutter-free and equipment, such as forklifts or pallet jacks, has pre-designated routes to prevent accidents.
4. Standardize (Seiketsu)
The Standardize principle states that consistent processes, procedures and guidelines should be established and followed to maintain efficiency.
To implement the Standardize principle:
- Document existing processes and procedures within the warehouse: This includes workflows, inventory management, order fulfillment, receiving, picking, packing and shipping processes. Take note of any variations or inefficiencies in these processes.
- Analyze the documented processes and identify areas where best practices can be established: This involves identifying the most efficient and effective ways of performing tasks, reducing waste and improving overall productivity. Benchmark against industry standards and seek input from employees who are directly involved in these processes.
- Create clear and concise work instructions for each task or process: These instructions should outline the step-by-step procedures, expected outcomes, quality standards and safety precautions. Standardized work instructions serve as a reference point for employees to consistently perform their tasks.
- Provide training for your warehouse staff: Train your staff on the newly established standardized work instructions. Ensure that employees understand the procedures, follow the guidelines, and are capable of performing their tasks according to the standard.
- Utilize visual cues: Use signs, labels, color-coded indicators or floor markings to visually represent the standardized processes and guidelines. These visual management tools help employees easily identify the correct procedures, locations, or materials, reducing errors and promoting adherence to the standard.
5. Sustain (Shitsuke)
The Sustain principle states that the first four S’s (Sort, Set in Order, Shine and Standardize) should be consistently maintained to create a culture of continuous improvement.
To implement the Sustain principle:
- Conduct regular audits: Identify any areas that need improvement and ensure standards are being maintained
- Provide ongoing training: Consistently reinforce the importance of 5S practices and ensure your warehouse operators know how to apply them
- Acknowledge warehouse employees: Reward your staff who maintain high standards to boost their morale and job satisfaction and encourage other operators to follow their lead
How To Implement Lean Warehouse Management
Once you’ve nailed down the steps to achieving a lean approach, the next step is to implement best practices into your daily warehouse operations.
To fully integrate the lean warehousing approach:
1. Audit Your Warehouse Processes
Auditing your warehouse processes is key to identifying inefficiencies and areas that need improvement in your warehouse.
- Define your objectives: These might include improving efficiency, reducing costs, ensuring safety compliance, enhancing customer service or identifying training needs. Clear objectives will help you focus on the audit.
- Create an audit checklist: Develop a list of areas to examine based on your objectives. This might include inventory management, order picking, packing and shipping, equipment maintenance, space utilization and employee training.
- Gather data: Utilize different methods to collect information, such as physical inspections, staff interviews, documentation review (like shipping records or safety logs) and data analysis (like order fulfillment times or error rates).
- Analyze the data: Look for patterns that indicate a problem. For example, if there are frequent stockouts of specific items during a certain season, this might indicate inadequate stock of fast-moving items.
- Benchmark your performance: Compare your performance against industry standards and/or against your past performance to look for areas that need improvement.
- Provide recommendations: Based on your findings, recommend improvements. This might include changes to procedures, equipment, warehouse layout or employee training.
- Present your findings: Prepare a report outlining your findings and recommendations, and present this to the relevant stakeholders.
2. Implement Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management
Just-in-time (JIT) is a type of inventory management that requires you to work closely with suppliers to ensure that raw goods arrive as soon as production is scheduled to begin.
Implementing JIT inventory management allows you to boost efficiency, eliminate excess inventory and reduce storage costs — goals that are in line with lean manufacturing.
To implement JIT inventory management in your warehouse:
- Collect historical sales data at a granular level (by consumer behavior or SKU, for example) to provide a detailed outline of your demand patterns.
- Develop strong relationships with your suppliers and involve them in your planning process. Communicate your demand forecasts with your suppliers and ensure they can meet your requirements in terms of quantity, quality and timing.
- Implement an inventory management software that automatically triggers purchase orders when your goods reach low inventory levels, so you don’t risk stockouts.
- Implement strict quality control measures in your operations and with your suppliers to prevent defective products.
3. Train Your Warehouse Employees
Implementing lean warehousing requires changing processes and restructuring your employees’ mindsets.
Training your warehouse employees is key to ensuring that everyone understands the principles of lean manufacturing and how to put them into practice.
To train your employees on lean warehousing practices:
- Provide a thorough orientation program for your new employees. The program might include an introduction to the principles of lean warehousing, for example, along with an overview of your company’s specific processes and procedures and a clear explanation of employee roles and responsibilities within the warehouse.
- Offer specific training sessions focused on lean warehousing principles and practices, such as the 5S methodology, value stream mapping, waste reduction techniques, visual management and problem-solving tools for continuous improvement.
- Provide hands-on training opportunities for your employees to apply lean concepts, such as mock simulations, role-playing exercises or actual work assignments.
4. Utilize Warehouse Automation
Automation can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy in your warehouse — characteristics that align with the lean approach.
Automated warehouse solutions include automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), robotic picking systems, and warehouse management systems (WMS) that can boost picking accuracy and speed.
5. Utilize Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
The lean journey doesn’t end once the initial improvements have been implemented — it’s a continuous process.
You can ensure continuous improvements by holding regular team meetings to discuss ideas or hosting formal kaizen events where your team works together to solve a particular problem.
Achieve Lean Warehousing With Modula Automated Warehouse Solutions
As a leader in automated storage solutions and warehouse management systems, Modula provides advanced solutions that can enhance productivity, efficiency and picking accuracy — primary goals that align with the lean warehousing approach.
Our automated solutions include:
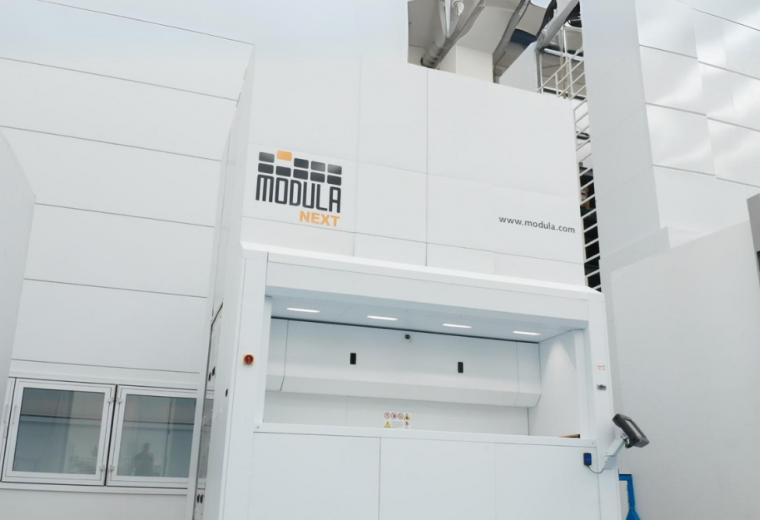
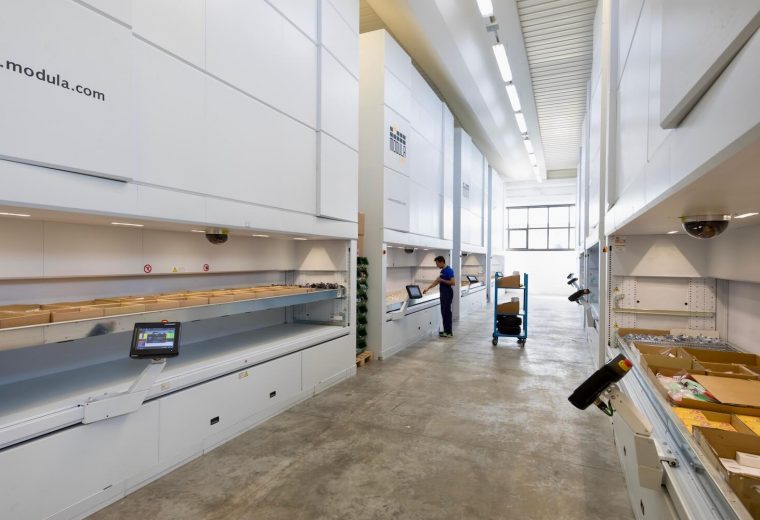
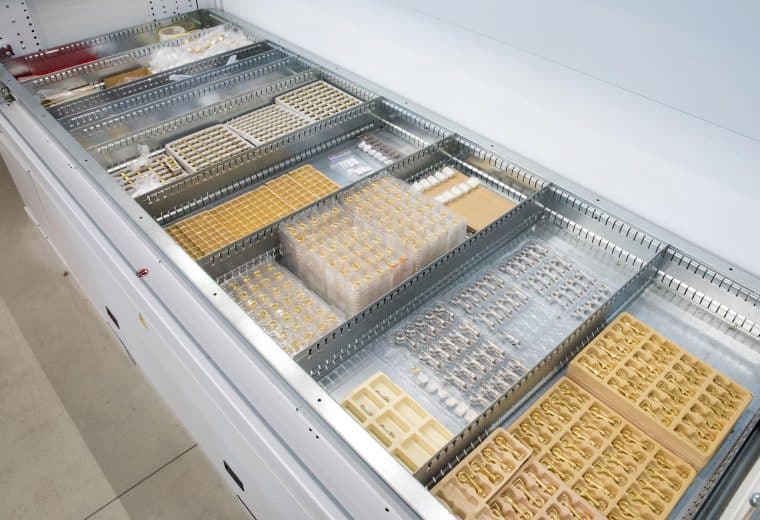
Modula Vertical Lift Modules
Modula Vertical Lift Modules (VLMs) maximize your existing warehouse space by utilizing your available ceiling height, boosting efficiency and capacity.
Modula VLM models include:
- Modula Lift: Perfect for storing industrial and spare parts; available in a wide variety of capacities and sizes.
- Modula Slim: Ideal for warehouses with limited floor space, thanks to its compact design.
Our VLMs allow you to:
- Save up to 90% of floor space by taking advantage of your available ceiling height
- Speed up order processing with a throughput of 140 trays per hour
- Increase picking speeds to over 300 lines per hour
- Enhance employee safety by removing the need for reaching high and low areas
- Safeguard your inventory thanks to a secure, enclosed system
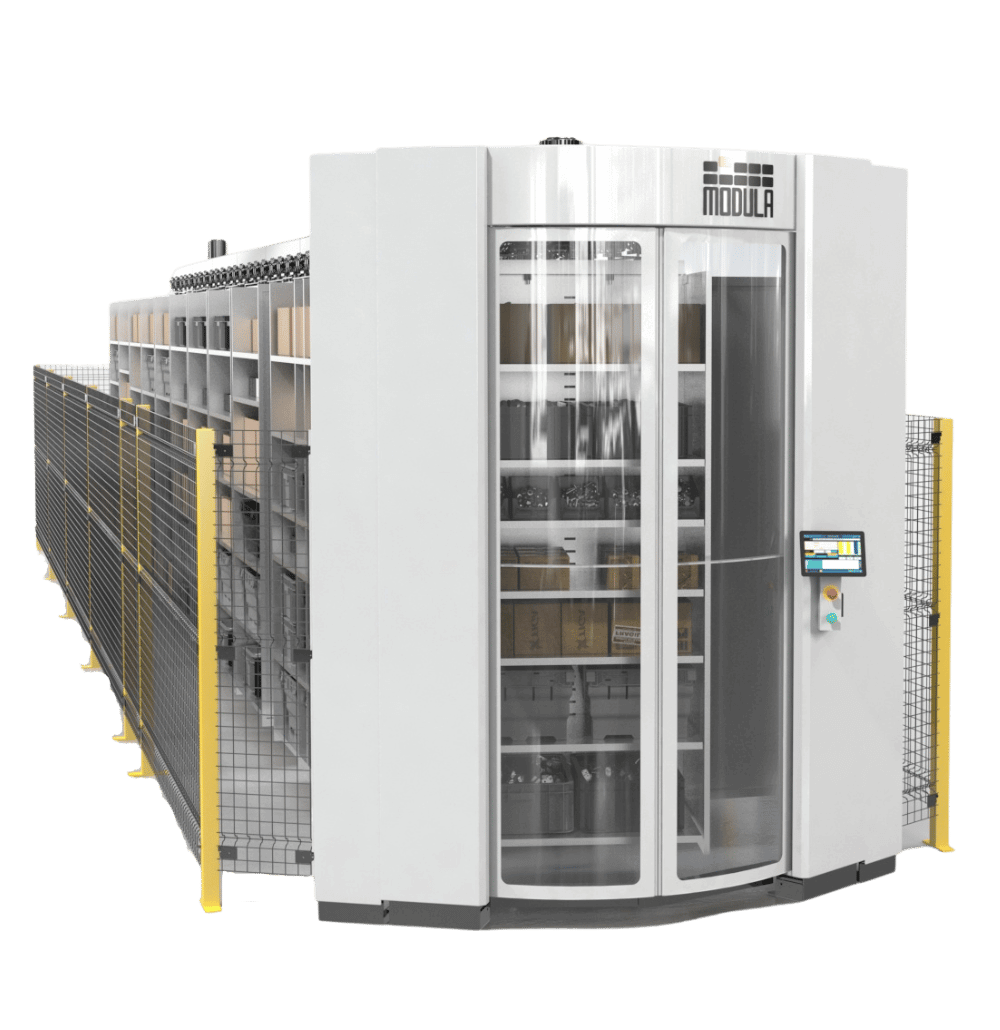
Modula Horizontal Carousel
The Modula Horizontal Carousel (HC) is the ideal automated storage solution for facilities where ceiling height is limited.
Our HC allows you to:
- Modify shelf spacing to store different goods
- Boost picking rates to 550 lines per hour per operator
- Achieve complete visibility of stock levels and orders
- Monitor picking operations in real time
- Achieve near-perfect picking accuracy, hitting 99% with our Put to Light Systems and barcode readers
Modula Picking Solutions
Modula picking solutions reduce the search time needed for navigating inventory and boost picking accuracy when handling large or individual orders.
Our Picking Solutions allow you to:
- Improve picking accuracy and speed using light devices that guide your warehouse operators to the right location
- Enhance inventory management with a comprehensive view of your current and forecasted stock
- Further drive order accuracy and efficiency when paired with our advanced automated storage solutions
Modula Warehouse Management System
Modula Warehouse Management System (WMS) enables you to monitor your inventory’s location and movement, giving you full insight into your stock levels.
Our WMS allows you to:
- Experience full inventory visibility
- Monitor and track stock levels and inventory movement
- Enhance accuracy when paired with Modula ASRS
Modula’s advanced storage solutions and warehouse management system allow you to implement a lean approach to your warehouse operations to optimize your storage space, improve your picking accuracy and boost your employee’s productivity and efficiency.










