What Is Inventory Turnover Ratio? [+ How To Calculate It]
To generate profit and cover expenses, you need to sell the products you purchase. This is where the inventory turnover ratio becomes crucial.
The inventory turnover ratio reveals how quickly inventory moves through your facilities.
Understanding your inventory turnover ratio helps you make smarter decisions about pricing, production, and inventory management. This insight can also help you keep an optimal amount of stock on hand and maintain a healthy bottom line.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to calculate your inventory turnover, define a good inventory turnover ratio, and discuss strategies to achieve a faster turnover rate.
Plus, we’ll introduce you to Modula’s warehouse management system (WMS) to help streamline your inventory management and seamlessly integrate with your existing ERP and DMS systems, further boosting your profitability.
What Is Inventory Turnover?
Inventory turnover is a warehouse KPI that tracks the time from the product acquisition phase until it’s sold.
A complete inventory turnover indicates that all purchased SKUs, excluding any losses due to damage or shrinkage.
Average stock smooths out fluctuations from unusual changes over specific periods, like days or months, providing a more reliable metric.
For instance, in seasonal sales, inventory levels of products, such as fresh Christmas trees and wreaths, spike before the season starts and drop significantly afterward. This reflects their temporary demand spike.
What Is Inventory Turnover Ratio?
The inventory turnover ratio measures how frequently a company sells and restocks its inventory within a specified period.
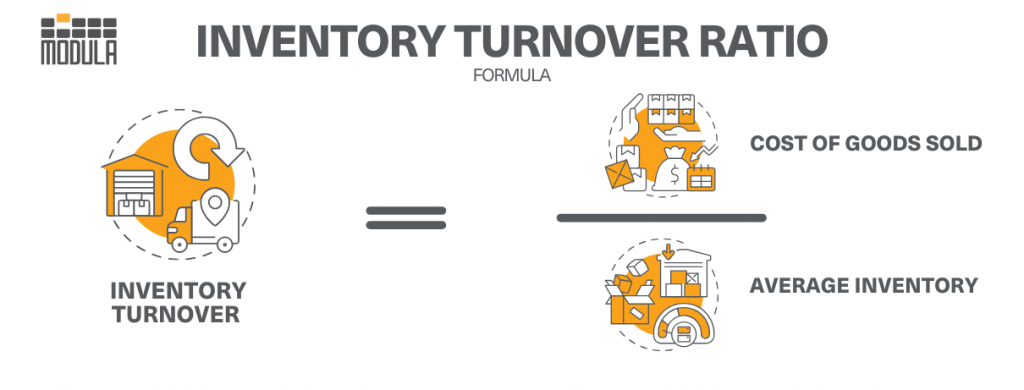
As a warehouse manager, you can calculate this metric by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory. You can also use the ratio to estimate the number of days it will take to sell existing inventory.
How To Calculate Inventory Turnover
Follow these three steps to calculate your inventory turnover:
- Determine the cost of goods sold (COGS) for the accounting period.
- Calculate the average inventory value by adding the beginning inventory to the ending inventory and then dividing it by 2.
- Divide the COGS by the average inventory to get the turnover rate.
The basic formula for the inventory turnover ratio is:
Inventory turnover = COGS / Average inventory value
What Is a Good Inventory Turnover Ratio?
For most industries, an ideal inventory turnover ratio falls between five and ten, suggesting that inventory is sold and replenished every one to two months.
This balance ensures adequate stock levels without the need for overly frequent reordering.
You might ask, “Can an inventory turnover ratio be too high?“
A higher turnover ratio is generally more favorable, as it indicates strong sales. However, an excessively high turnover can actually harm your financial standing and set back business performance.
Think of it this way: if your inventory turns over too quickly, it might lead to frequent stockouts, forcing you to rush orders and possibly incur higher costs or miss sales opportunities.
This situation can overextend your resources and disrupt operational efficiency, negatively impacting customer satisfaction.
Maintaining a balanced turnover rate ensures you have enough inventory to meet customer demand without the negative effects of overexerting your supply chain.

3 Common Uses of Inventory Turnover
Inventory turnover ratios can help streamline various business operations, including inventory management, pricing strategies, supply chain execution and sales, contributing significantly to overall company success.
Turnover Trends
Inventory turnover ratios serve as an important tool to identify emerging market trends and outdated or slow-moving stock.
This provides early insights into whether to increase or cut back on production or marketing efforts for specific product lines or brands and optimizes sales opportunities.
Segments and SKUs
Inventory turnover is generally calculated at the SKU level, or at the segment level for more precise control over stock. This process, known as inventory segmentation, categorizes SKUs according to specific business-relevant metrics such as sales velocity, seasonal relevance, or profitability.
For example, a retailer might classify products into categories such as electronics, apparel, or home goods to analyze and compare performance across these distinct sectors within their portfolio.
This allows for targeted strategies to strengthen sales and inventory efficiency in each category.
80/20 Rule
The Pareto principle, which states that 80% of a company’s sales often come from 20% of its SKUs, is broadly applicable in business and life and is ideal for inventory management.
Loss leaders — products priced low or at a loss to attract customers — are crucial for drawing people into both online and physical stores. There, customers may purchase additional, more profitable items. Identifying and maintaining sufficient stock of these key products is essential.
Tips To Improve Your Inventory Turnover
Now that you understand how to utilize your inventory turnover ratio, here are strategies to amplify your turnover:
Optimize Your Supply Chain
Select suppliers for their competitive pricing and dependable, fast delivery, particularly for essential or high-demand products.
Eliminating inefficiencies in your supply chain, such as redundant processes, excessive inventory and slow-moving logistics, can help boost your sales and profitability.
Revise Your Pricing Strategy
Increase margins on high-demand items and clear out old or obsolete inventory to free up capital.
If some of your products consistently fail to sell, consider making a tax-deductible donation or selling them through alternative channels like clearance outlets or pop-up sale events.
Consider Product Bundling
When implementing product bundling, you’re grouping compatible items to attract more customers. For instance, a tiered pricing strategy helps move slow-selling products faster by pairing them together, aiming to clear inventory while still making a profit.
Additionally, explore volume discount bundles for selling multiples of the same item, such as buy-two-get-one-free deals that offer consumers more value.
Boost Your Industry Standing
Ensure your inventory turnover aligns with industry standards. You should also seize opportunities to improve your competitive positioning by monitoring inventory trends, adapting to market demands, and leveraging data analytics to forecast future sales and manage stock levels effectively.
When you strategically manage your inventory, you can gain more market share and improve your industry ranking.
Conduct Accurate Forecasting
Closely monitor seasonal and occasional products as they significantly impact your inventory. Use this data and your target demographics to refine your annual and quarterly forecasts.
With accurate forecasts, you can allocate resources more effectively by investing in high-demand items and reducing or eliminating orders for less popular products.
Collaborate With a 3PL
Outsourcing logistics, storage and distribution to a third-party logistics (3PL) streamlines operations, reduces overhead costs and enhances delivery times.
This efficiency quickens sales cycles and stabilizes stock replenishment, boosting your inventory turnover rate.
In addition, a 3PL provides expertise in inventory management and advanced tracking and forecasting technologies, optimizing your inventory levels and ensuring product availability when and where needed.
Automate Purchase Orders
Implement automation to reinforce efficiency and cut costs. A warehouse management system (WMS) establishes trigger reorder points based on predefined inventory levels, ensuring timely orders for new stock as needed.
This prompt replenishment can help your operations maintain a consistent flow of goods, aligning with sales velocity and avoiding excessive holding costs.

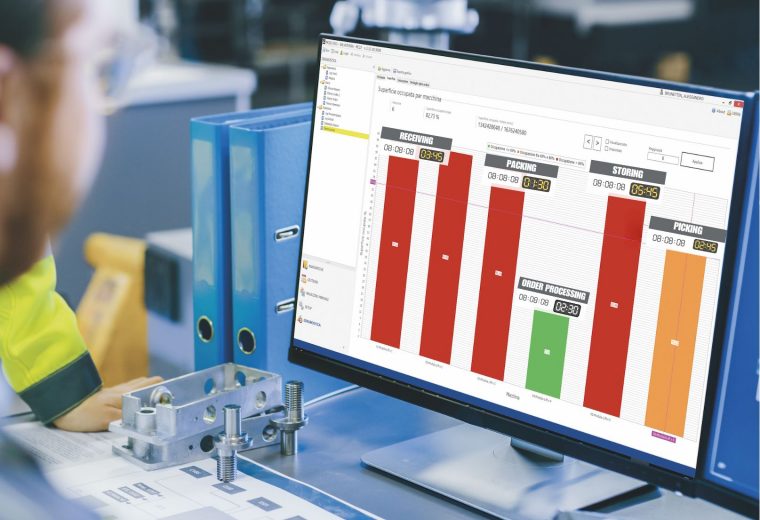
Augment Your Inventory Turnover With Modula’s Warehouse Management System (WMS)
Inventory management software provides numerous capabilities that enhance and streamline your inventory practices.
For instance, it enables your company to adopt a perpetual inventory system that supports a continuous, real-time inventory record.
When you integrate an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system with your WMS, you can better maximize supply chain operations, manage SKUs, and automate purchase orders, among other functions.
The Modula Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a comprehensive inventory management platform, crafted to manage Modula’s automated storage retrieval systems or function independently in conventional warehouses.
Recognized as one of the most sophisticated and user-friendly software options available, Modula WMS integrates smoothly with nearly all DMS and ERP systems. This integration guarantees efficiency and precision in operations such as receiving, selecting, and storing products.