Automated Sortation Systems [Types, Application & Benefits]
Every second counts in a busy warehouse.
As order volumes grow and delivery expectations tighten, the ability to sort thousands of items accurately and efficiently is no longer a nice-to-have—it’s a necessity. That’s where automated sortation systems come in.
These automated material handling solutions identify, route, and direct items based on destination, size, weight or other criteria, further reducing manual labor and minimizing errors along the way.
Using a combination of conveyors, chutes, diverter,s and robotic arms, they help optimize warehouse operations and improve overall order processing speed.
In this guide, we’ll explore:
- The main types of sortation systems
- Their key benefits
- Their common applications across different industries
3 Types of Sortation Systems and How They Function
A sortation system integrates different technologies designed to sort large volumes of inventory with efficiency and speed.
Here’s how they operate:
Linear Sortation Systems
Linear sortation systems employ conveyor systems where items travel along a linear path.
These systems incorporate mechanisms like pop-up wheels or arms to divert items to the left or right into sorting bins or additional conveyors, based on automated decisions.
- Best for: Medium-speed applications, simple layouts, limited space
- Common technologies: Pop-up wheel sorters, pusher sorters
Pusher Sortation Systems
They feature a simple conveyor setup with a series of pusher arms spaced along the path. These arms extend to transfer items from the main conveyor to a secondary location as directed by the automation system.
- Best for: Flat, lightweight items or for lower throughput environments.
- Strength: Simple, cost-effective, and easy to maintain
Loop Sortation Systems
They consist of conveyors arranged in a continuous loop. Ideal for operations using tilt-tray and cross-belt sorters.
In these systems, items are placed on trays or belts that circulate around the loop. At designed points, trays or belts adjust their orientation or activate to direct the item into a designated chute, tote or bin.
- Best for: High-speed, high-volume environments with many sorting destinations
- Common in: E-commerce, retail, large distribution centers
| SYSTEM TYPE | HOW IT WORLS | BEST FOR | COMMON TECHNOLOGIES |
| Linear Sortation Systems | Items move along a straight conveyor path and are diverted using pop-up wheels or diverters. | Medium-speed operations, simple layouts, limited space | Pop-up wheel sorters, pusher sorters, general warehousing |
| Pusher Sortation Systems | Pusher arms extend to transfer items from the main conveyor to a secondary location. | Flat, lightweight items or lower throughput environments | Postal sorting, light manufacturing, cost-effective setups |
| Loop Sortation Systems | Items ride on trays or belts circulating in a loop, diverted at designated points. | High-speed, high-volume environments with many destinations | Tilt-tray and cross-belt sorters, e-commerce, large DCs |
The Importance of Sortation Systems in Warehouse Automation
Automated sortation is the process of identifying items on a conveyor belt or other transport mechanism and diverting them to various destinations within a warehouse based on predefined criteria.
The sortation process is tailored to meet the specific needs of a facility and can sort items by various characteristics such as size, weight, destination or other factors relevant to your warehouse operations.
A sortation system classifies items on a conveyor belt then directs them to different areas in a warehouse based on predefined criteria, such as size, weight, destination or priority.
These systems play a crucial role in different processes, including replenishment, order fulfillment, kitting, cross-docking and returns handling.
Sortation systems can be manual or fully automated.
Manual sortation systems often rely on human intervention, with workers physically sorting or assisting in the sorting process.
On the other hand, automated sortation systems utilize advanced technologies such as sensors, conveyors, barcode scanners and software to automatically identify and route inventory to their designated locations without human intervention.

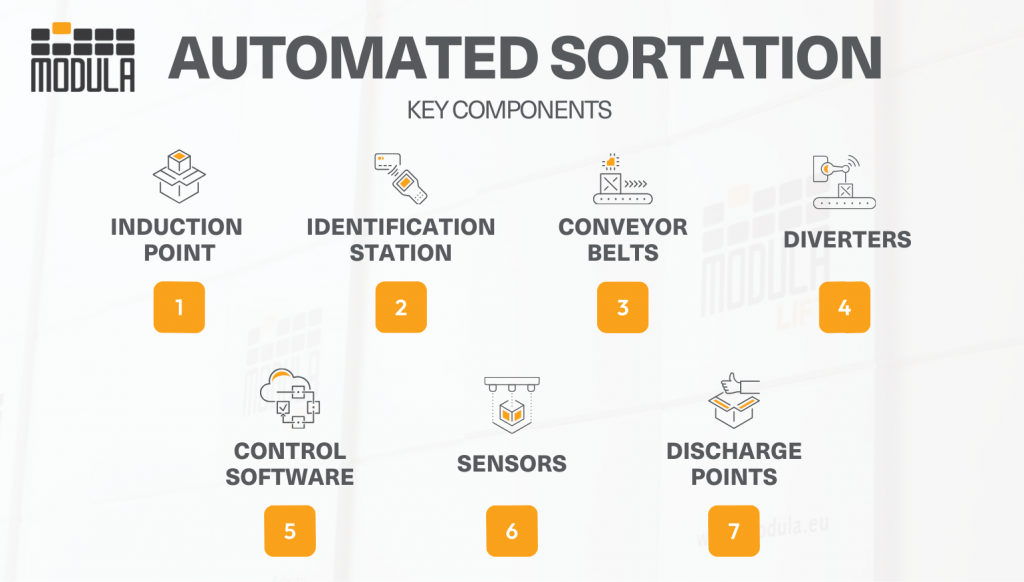
Key Components of a Sortation System
A sortation system consists of several key components that work together to efficiently sort and route items to their destinations.
- Induction points: This is where inventory enters the sortation system, marking the starting point of the automated sorting process.
- Identification stations: Sortation systems utilize RFID or barcode scanners to identify items and feed information into a control system.
- Conveyor belts: These transport items through the system, connecting all components in the sorting process.
- Diverters: These physically redirect items off the conveyor to destinations such as chutes, containers for consolidated orders ready for outbound shipment, or other conveyors leading to specific areas.
- Sensors: These are used throughout the system to detect item presence, position, size, and other critical data needed for proper sorting
- Control software: This leverages scanned information and programmed logic to determine the correct path for an item within the warehouse.
- Discharge Points/Outfeeds: These are the final destinations where sorted items are delivered, such as bins, chutes, or other conveyors.
Common Sortation System Applications
Multiple industries and sectors take advantage of automated sortation systems to enhance their sorting and distribution processes.
Courier and Logistics
Sortation systems are essential in courier and logistics centers for sorting and directing packages to different locations, such as specific cities, regions or delivery routes.
These systems boost the speed and efficiency of package distribution, decrease errors and refine overall delivery performance.
Retail
Sortation systems play a crucial role in eCommerce and retail distribution centers by managing the high volume of incoming orders.
These systems effectively sort and direct individual items or packages to their intended destinations, ensuring quick and precise order processing.
Food and Beverage Distribution
Sortation systems in food and beverage distribution centers efficiently manage the flow of products, prioritizing items based on specific needs such as temperature control for dairy or expiration dates for perishables like fruits and vegetables.
These systems further preserve quality, minimize waste and prevent spoilage.
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare
From over-the-counter medications to specialized medical equipment, sortation systems in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors manage the distribution of a wide range of products.
They ensure the precise sorting and timely delivery of essential items to hospitals, clinics, pharmacies and patients, supporting the critical infrastructure of healthcare services.
Manufacturing and Production
Sortation systems are essential on production lines for items such as automotive parts and electronics, where they streamline the flow of items through assembly, packaging and shipping stages.
These systems significantly enhance workflow efficiency and boost productivity.
Airport Baggage Handling
Sortation systems automate the routing and sorting of luggage by using advanced scanning and conveyor technologies to read baggage tags and direct each piece to the appropriate flight, gate or carousel.
This precise coordination ensures accurate loading of luggage onto the correct aircraft, increases baggage handling efficiency and lowers the likelihood of misrouted or lost luggage.
Postal Services
Sorting machines are utilized in postal operations to automate the sorting and handling of mail.
They read addresses and categorize letters, envelopes and parcels according to their postal codes or other predetermined criteria.
This allows postal services to process large volumes of mail with greater efficiency.
Key Benefits of Automated Sortation Systems
Automated sortation systems provide valuable benefits for optimizing warehouse operations, including:
- Increased efficiency, accuracy and speed: Automated sortation systems handle high volumes of items quickly, substantially reducing the time goods spend moving from receiving to shipping and significantly outperforming manual sorting methods.
- Enhanced order accuracy: The precision of automated systems reduces the potential for errors, decreasing the incidence of costly returns.
- Better customer satisfaction: Ensuring accurate and timely shipments, these systems revamp service levels and boost customer satisfaction.
- Impact on order fulfillment: The true value of automated sortation systems lies in their ability to optimize the order fulfillment process, directly influencing overall customer satisfaction.
- Lower operational costs: Enhanced efficiency enables more effective use of labor and resources, leading to lower operational expenses.
- Scalability and adaptability: Automated sortation systems can be easily scaled or reconfigured to handle changes in order volume, product types, or fulfillment strategies, making them a flexible solution for growing and evolving warehouse operations.
Factors To Consider When Choosing the Right Automated Sortation System
When choosing a sortation system, consider the following factors:
- Throughput needs: The average and peak quantities of items to be sorted per hour or day should align with the system’s capabilities.
- Item features: The size, shape, and weight of the items will determine their compatibility with various sortation methods.
- Adaptability and expansion potential: The system should be flexible to accommodate shifting business requirements and scalable for anticipated growth.
- Integration features: Assess how easily the system can integrate with existing warehouse management system (WMS) and other technologies.
- Budget: Weigh the initial investment costs against the potential for long-term savings and improved efficiency.
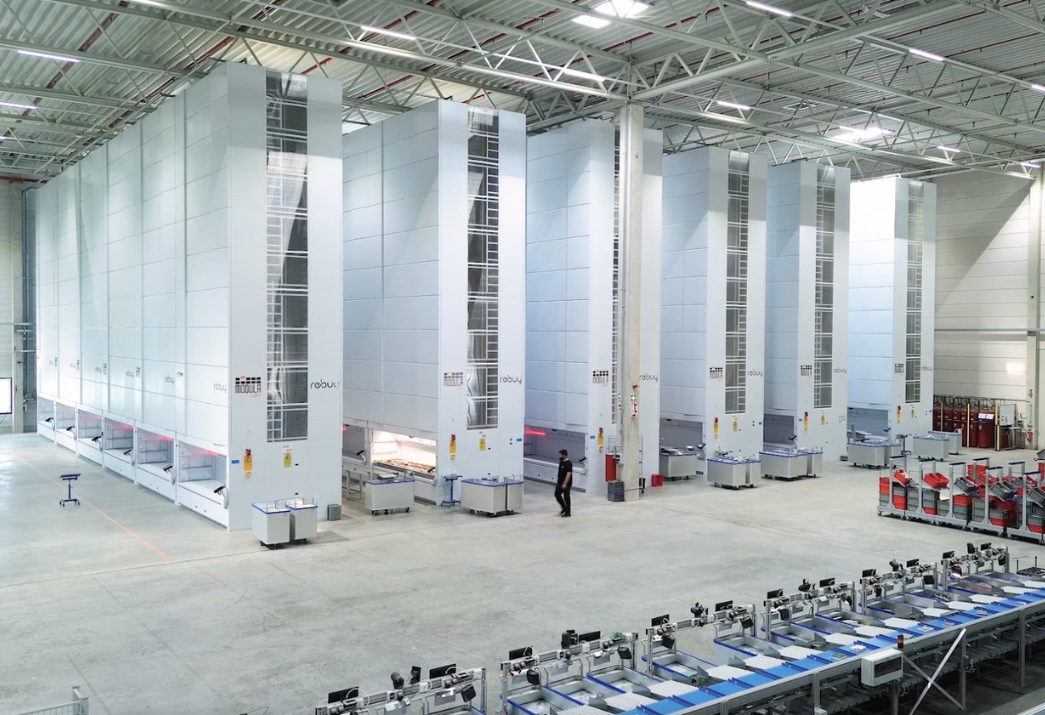
Optimize Logistics and Inventory Management With Modula ASRS
Automated sortation systems and Modula automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) work together to streamline warehouse efficiency and accuracy.
Here’s how they integrate and function in a logistics setting:
- Storage and retrieval with Modula ASRS: Modula systems automatically store and retrieve items based on software commands. They use vertical lift modules (VLMs) and horizontal carousels to maximize space utilization and improve accessibility. In warehouses, these systems efficiently manage high-density inventory with precision.
- Integration: Once the Modula ASRS retrieves items, automated sortation systems take over to direct them to the appropriate processing, packing, or shipping areas. These systems optimize the movement of goods and reduce manual handling.
- Sorting and routing: Automated sortation systems use barcode scanners, RFID readers and optical recognition technology to identify items and determine their destinations. Conveyors or robotic transport systems then route the items efficiently, optimizing workflow and preventing bottlenecks.
- Seamless coordination: The integration between Modula ASRS and sortation systems enables real-time data exchange and operational synchronization. This ensures items move smoothly from storage to sorting and dispatch, minimizing delays and human errors.
- Software and control systems: Both Modula ASRS and automated sortation systems are integrated with a WMS, which oversees inventory, order processing and fulfillment operations. This seamless integration facilitates real-time data exchange between the sortation system and the WMS, eliminating delays and ensuring accurate tracking and timely updates of item statuses within the inventory system.
Reach out to us and discover how our integrated solutions can streamline your warehouse operations, enhance efficiency, and improve accuracy across your supply chain.












