2025 Guide to Pallet Storage [+ Tips for Efficient Handling]
Pallet storage provides an economical and efficient way to organize and transport goods. This system is popular in logistics and eCommerce due to its cost-effectiveness and efficiency in storing and transporting goods.
We’ll cover everything about pallet storage, including types, benefits and common challenges. Plus, we’ll explain how Modula’s automated pallet racking systems can enhance your warehouse processes.
What Is Pallet Storage?
Pallet storage solutions are warehouse storage systems that accommodate large bins or boxes on pallets to optimize space and organization.
Pallets, which are typically made from wood, metal, or plastic, are durable and secure platforms for stacking and storing goods.
Manufacturers usually build pallets in a double-deck configuration, with a top deck supported by three or four stringers. Stringers, which are supporting structures, bear the weight of the load and allow forklifts or trolleys to lift the pallet.
Warehouse employees usually stack the pallets on racks or shelves and store them in multiple configurations.
Types of Pallets According to Their Material
Pallets come in various materials, each suited for specific needs and applications.
- Wooden Pallets: Wooden pallets are durable and easy to repair. Manufacturers can customize them to different sizes, and they dominate the market with approximately 90% to 95% of the market share.
- Presswood Pallets: Presswood pallets, or molded wood pallets, are made by molding wood fibers from wood byproducts under high pressure with resin. These woodchips undergo heat treatment to high temperatures, making them often IPSM15 compliant.
- Plastic Pallets: Resistant to moisture and chemicals, plastic pallets are ideal for clean environments or international shipping to prevent pest contamination. They’re durable and easier to clean and disinfect than wooden pallets. Additionally, they are 100% recyclable.
- Metal Pallets: Metal pallets are durable and strong, making them ideal for heavy or bulky items. However, their durability also makes them heavier and more expensive than wooden or plastic pallets.
- Cardboard Pallets: Cardboard pallets are lightweight and disposable, offering a cost-effective solution for one-way shipments.
Common Pallet Sizes
The size of a pallet directly influences its capacity and compatibility with various transportation systems. Additionally, the destination, size, and weight of your goods dictate the required pallet size, which in turn impacts shipping costs.
Common popular pallet storage sizes include:
Euro Pallet Sizes
The European Pallet Association specifies the typical Euro pallet as measuring 31.5 in × 47.2 inches (1200mm x 800mm), marked with “EPAL” or “EUR.”
Additionally, the Euro pallet is one of the pallet types standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
European industry and logistics primarily use these pallets to streamline goods flow and consolidation during transport and storage. The dimensions of the Euro pallet correspond to the 2400mm width of truck wagons, containers and trailers, allowing for optimal use of the load space.
Other Common Euro Pallet Sizes:
EUR 2: 47.2 x 39.4 inches (1200mm x 1000mm) – Suitable for bulk goods and heavy loads.
EUR 3: 39.4 x 47.2 inches (1000mm x 1200mm) – Used for industrial applications.
EUR 6: 31.5 x 23.6 inches (800mm x 600mm) – Smaller pallet often used for retail and point-of-sale displays.
UK Pallet Sizes
In the United Kingdom, standard pallets measure 47.2 x 39.4 inches (1200mm x 1000mm). They are compatible with most U.K. warehouse racking and forklifts and are optimized for transport within the UK. These pallets are 20% larger than Euro pallets.
North American Pallet Sizes
The most common pallet size in North America is the GMA (Grocery Manufacturers Association) pallet, measuring 48 x 40 inches (1219 x 1016 mm).
Other Common North American Pallet Sizes:
- 42 x 42 inches (1067mm x 1067 mm) – Common in the food and beverage industry.
- 48 x 48 inches (1219mm x 1219 mm) – Often used for chemical and drum storage.
Globally recognized pallet sizes include
- 45.87 x 45.87 inches (1165mm x 1165mm) – Widely used in Australia
- 43.31 x 43.31 inches (1100mm x 1100mm) – Prevalent in Asia
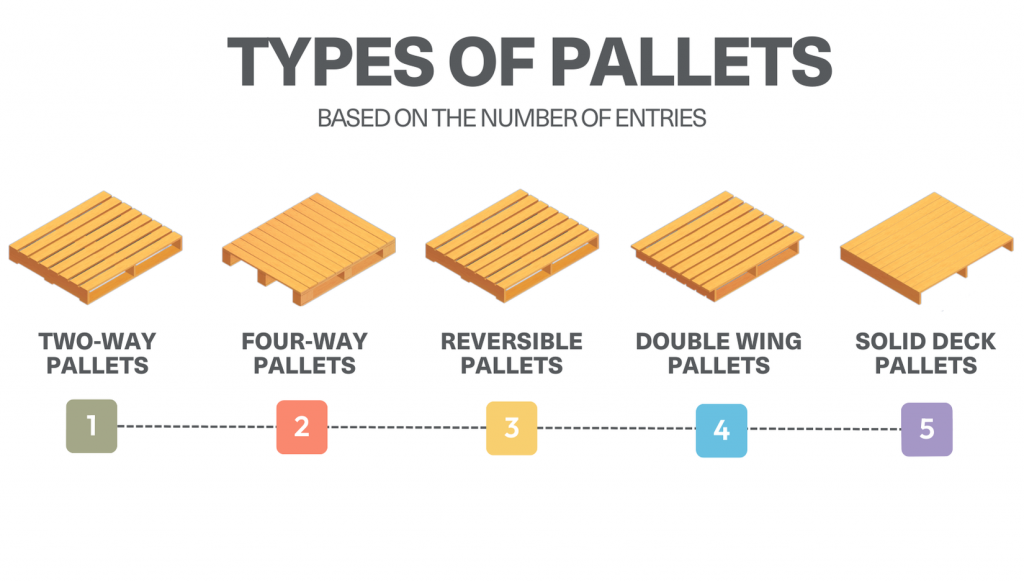
Types of pallets based on the number of entries
Pallets can be categorized based on the number of entry points available for forklifts or pallet jacks. This design aspect impacts how easily pallets can be accessed, lifted, and transported during warehouse operations.
Stringer Pallets (Two-Way Pallets):
A 2-way pallet has two entry points, meaning forklifts can lift it from only two opposite sides. While they offer less access than 4-way pallets, they are often lighter and more cost-effective, making them a popular choice for lighter loads and basic storage needs.
Block Pallets (Four-Way Pallets):
A 4-way pallet has four entry points, allowing forklifts and pallet jacks to access it from all four sides. This design makes handling easier and more flexible, which is why 4-way pallets are widely used in warehouses for efficient storage and transport.
Double-Face Pallets:
A double-face pallet has boards on both the top and bottom, providing extra strength and stability. Some double-face pallets are reversible, allowing use from either side, while non-reversible ones have a designated top and bottom for load-bearing.
Double-Wing Pallets:
A double-wing pallet has top and bottom boards that extend beyond the stringers or blocks on both sides, creating a larger surface area for carrying oversized items. However, the extended edges make them less durable for heavy loads.
Solid Deck Pallets:
A solid deck pallet has a continuous, flat top surface without gaps. This design prevents smaller items from falling through and is easy to clean, making it ideal for industries where hygiene matters, such as food and pharmaceuticals.
How To Choose the Right Pallet Storage Solution
When selecting a pallet storage solution for your warehousing needs, consider the product’s weight, dimensions, and fragility, as well as its storage or transportation requirements.
Additionally, assess the shipping conditions and any specific requirements of the destination country or region.
You should also balance the pallet’s quality with its cost-efficiency. While more affordable options may be tempting, investing in durable pallets can reduce damage and replacement costs in the long run.
For instance, in Europe, choosing heat-treated wooden Euro pallets can be beneficial due to the European Pallet Pool system and compliance with IPSM 15 standards.
On the other hand, in facilities that require clean, washable surfaces, plastic pallets might be the better choice.
Key Benefits of Pallet Storage
Pallet storage offers a cost-effective, organized, and efficient method for storing and transporting goods.
Here’s a quick rundown of its key benefits:
- Cost-effective: Pallet storage decreases handling and transportation costs, making it an affordable choice for moving inventory.
- High capacity: Thanks to their durable construction and design, pallets can support several thousand pounds. They enable efficient storage and transportation of heavy loads while maintaining stability and safety.
- Easy to manage: Unlike other advanced warehouse storage solutions, pallet storage solutions require minimal training for your warehouse employees to manage effectively.
Challenges of Using Manual Pallet Storage Solutions
Some challenges associated with using manual pallet storage solutions include:
- Mold growth: Stacking pallets too tightly can hinder effective air circulation and lead to moisture buildup. Wooden pallets are particularly susceptible to mold when exposed to moisture. This compromises the integrity of the pallet, damages stored goods and poses health risks in the warehouse.
- Space inefficiency: Although pallets optimize vertical storage, they require large aisles for forklift and worker access. This layout often results in inefficient use of floor space, especially in smaller warehouses where maximizing every square foot is crucial.
- Potential product damage: Overloading pallets may cause damage, such as broken boards or protruding nails. These defects can harm inventory and lead to workplace injuries, making regular upkeep and inspection necessary to maintain safety.
FAQs About Pallet Storage
What is the stacking limit of pallets?
The ideal stacking limit of pallets shouldn’t exceed 15 feet in height.
However, this limit can vary depending on the stability of the materials on the pallets. If the items are stable and sturdy, multiple full pallets can be stacked higher.
Keep in mind that your warehouse employees should only handle these tall stacks with the proper equipment.
How can you secure loose inventory on pallets to prevent accidents in the warehouse?
To secure loose inventory on pallets and prevent accidents in the warehouse, use the following methods:
- Stacking Patterns: Utilize interlocking or brick stacking patterns for the boxes to add stability and prevent shifting.
- Stretch Wrapping: Apply plastic stretch wrap around the items on the pallet. This holds the items tightly together and prevents movement during transport or storage.
- Strapping: Use straps or bands to secure the items to the pallet. This is particularly effective for heavier or irregularly shaped items that might shift more easily.
- Edge Protectors: Place edge protectors at the corners and along the edges of boxes to prevent damage from straps and stabilize the load.
- Load Binders: Use load binders on top of the load to compress and secure the items firmly.
- Shrink Wrapping: For additional security, especially for fragile items, use shrink wrap to encase the entire pallet.
How often should you inspect pallets for wear and tear?
It’s advisable to schedule professional inspections by a health and safety executive (HSE) at least once a year.
However, regular internal inspections are equally important to ensure your pallets remain in optimal condition and to catch any signs of wear and tear before they become a safety hazard.
- Daily Checks: Quick visual checks should be done daily, especially for pallets in active use, to spot any immediate or obvious issues like broken planks or protruding nails.
- Detailed Monthly Inspections: Conduct a more thorough monthly inspection to assess the overall condition of the pallets. Watch out for cracks, warping or any structural weaknesses.
- Annual Audits: Perform an annual review of your entire pallet inventory to determine the need for repair or replacement.
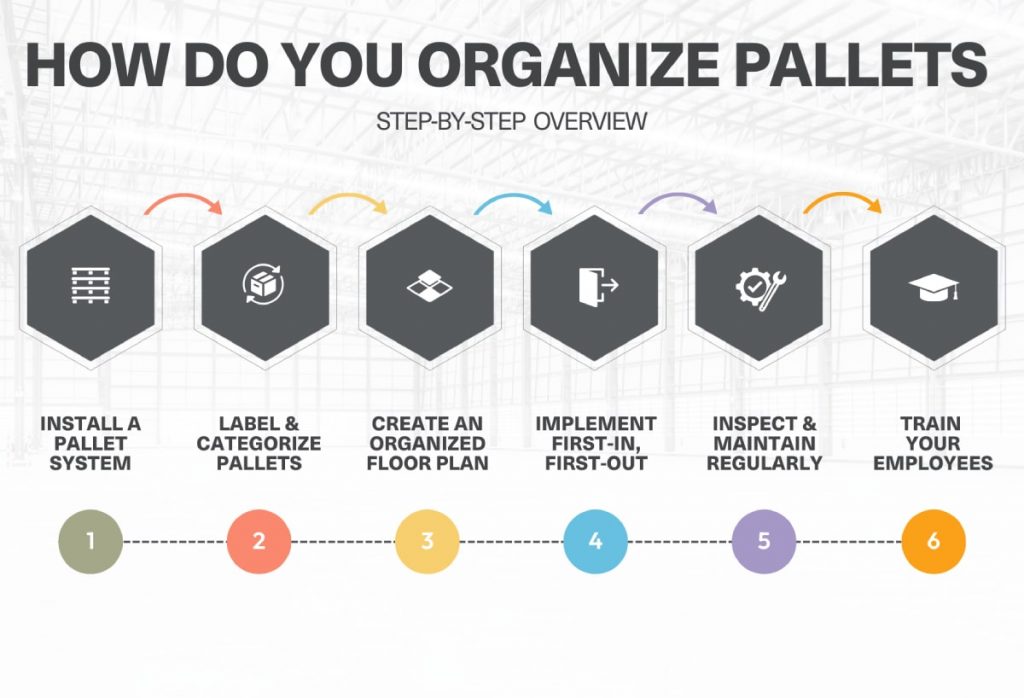
How do you organize pallets in a warehouse?
Organizing pallets in a warehouse involves several key steps to ensure efficiency, safety, and optimal use of space:
- Install a pallet racking system: Maximize vertical storage space by setting up a suitable pallet racking system, such as selective, drive-in or push-back, depending on your inventory needs.
- Label and categorize pallets: Clearly label each pallet and assign it to a specific location within the warehouse. Organize pallets by product type, size or frequency of use for easy access.
- Create an organized floor plan: Design an efficient layout with designated areas for receiving, storage, picking and shipping. Make sure your aisles are wide enough for forklifts and pallet jacks to pass through, and there’s sufficient space for safe loading and unloading operations.
- Implement First-In, First-Out (FIFO): Manage inventory by applying a FIFO system, ensuring older stock is used or shipped before newer stock to prevent obsolescence or spoilage.
- Inspect and maintain regularly: Regularly inspect your pallet racking system and equipment, replace damaged pallets and address any structural issues, such as bent beams, to maintain safety.
- Train your warehouse employees: Provide extensive training for all warehouse staff on pallet handling and safety protocol to help reduce the risk of accidents, such as overexertion.
Explore Modula Pallet for Efficient Ground-Level Pallet Handling
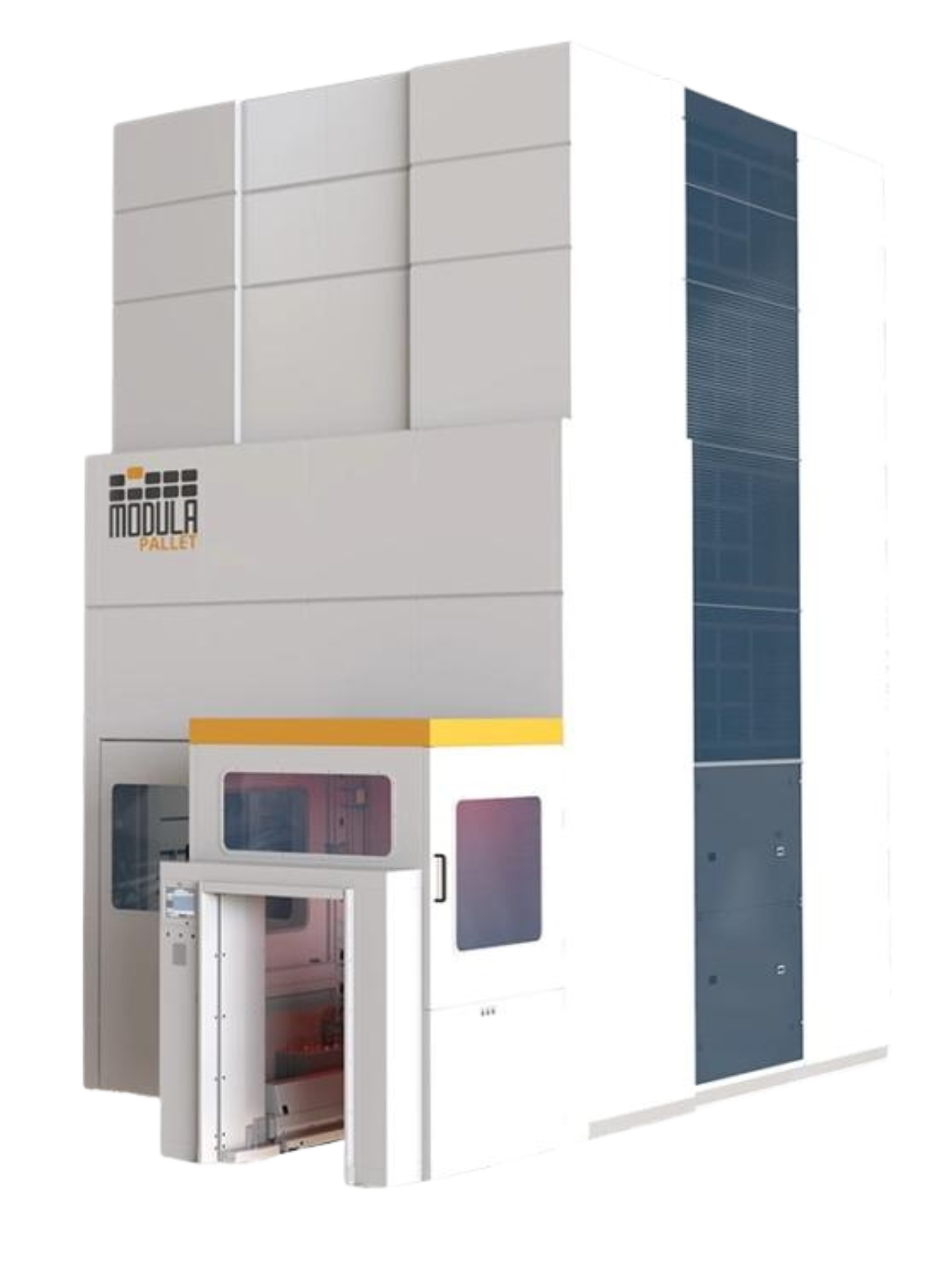

Modula Pallet is a cutting-edge warehouse solution that safely manages euro pallets (1,200mm x 800mm) right from the ground, eliminating the need for forklifts.
This system operates entirely at ground level, maximizing vertical space and minimizing the risks when it comes to lifting and storing items at height.
Designed for efficiency, the Modula Pallet offers flexible storage options.
It supports piece picking through a side window bay and can handle a variety of storage needs, including bulk products, pallets and goods without pallets.
Contact us
Need more details about pallet storage and how our storage solutions can help? Contact us to see how our technology can benefit your operations.






