Complete 2026 Guide to Pharmaceutical Compliance [+ FAQs]
As the U.S. pharmaceutical market grows from $634.32 billion in 2024 to an expected $883.97 billion by 2030, the need for sophisticated warehouse infrastructure is intensifying.
These warehouse systems must uphold strict regulatory standards, manage temperature-sensitive products with precision and support rapid, large-scale distribution, all while maintaining pharma compliance.
That’s why cold storage solutions are designed specifically for these needs, making it easier to manage the cold chain while staying efficient, compliant, and ready for audits.
In this guide, we will:
- Discover the core regulatory standards that govern pharmaceutical storage and distribution in the U.S
- Identify the most common risks in the pharmaceutical cold chain
- See how cold storage systems help pharmaceutical facilities maintain product integrity and optimize high-stakes operations
Understanding Pharmaceutical Compliance Requirements in the U.S.
Pharmaceutical warehouses in the U.S. operate under some of the strictest regulatory standards of any industry.
Pharmaceutical compliance is non-negotiable as it’s essential to ensure patient safety, product integrity, and regulatory approval.
Below are the core pharma compliance standards that every pharmaceutical warehouse must follow:
FDA Regulations
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees pharmaceutical storage through several key regulations:
- 21 CFR Part 211 (cGMP): Current Good Manufacturing Practices are the gold standard. For warehousing, this mandates controlled conditions for storage, validated equipment, comprehensive audit trails for every action, and restricted access to sensitive zones.
- 21 CFR Part 11: For facilities using automated systems, this regulation governs electronic records and signatures. It requires secure, time-stamped, and unalterable digital records, equivalent to traditional paper documentation.
- Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA): Mandates a system to identify and trace prescription drugs as they move through the U.S. supply chain, requiring robust tracking and audit capabilities within the warehouse.ses.
USP <1079> and Temperature Control Standards
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP), while not a regulatory agency, sets critical, industry-wide guidelines. USP General Chapter <1079> outlines Good Storage and Distribution Practices, covering key areas such as:
Temperature mapping and equipment validation
Humidity control
Facility design and maintenance
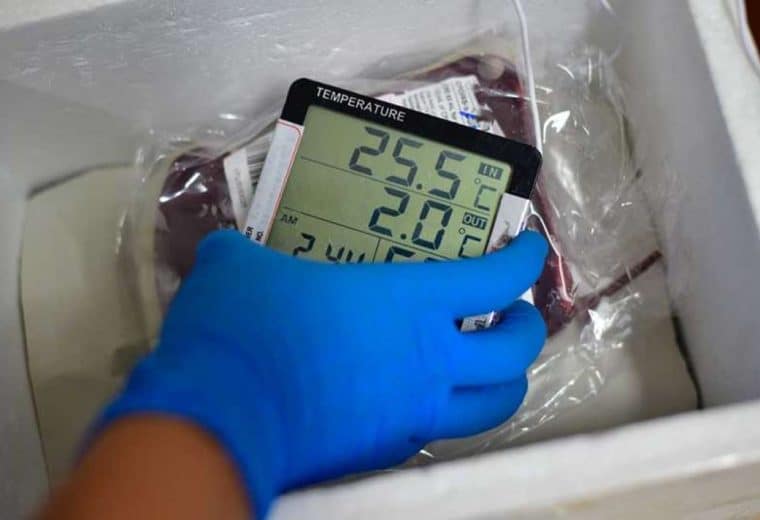
For temperature-sensitive products, maintaining specific ranges is non-negotiable. The primary standards are:
- Refrigerated: Maintained between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F)
- Frozen: Typically maintained between –25°C and –15°C (–13°F to 5°F)
Even minor deviations can compromise product safety and efficacy, making compliance more than just record-keeping. It demands validated cooling systems, backup power, and immediate alerts for any temperature excursions.
Equipment Validation (IQ/OQ/PQ)
To meet GMP standards, any automated system must undergo a formal, three-stage validation process:
- Installation Qualification (IQ): Confirms the system is installed correctly and according to the manufacturer’s requirements.
- Operational Qualification (OQ): Verifies the system operates according to its functional specifications in all anticipated ranges (for example, reliably maintains the required temperature).
- Performance Qualification (PQ): Documents that the system performs consistently and reliably under actual, real-world operational conditions.
Common Cold Chain Challenges in Pharmaceutical Warehousing
Pharmaceutical products must be stored and handled with extreme care. Any temperature excursion, data gap, or security breach can compromise product safety and lead to regulatory trouble.
Here are the top compliance and integrity risks every pharmaceutical warehouse needs to manage:
Environmental Risks: Temperature, Contamination, and Infrastructure
A) Temperature Changes During Handling and Transit
Even short-term deviations from required ranges, typically 2°C to 8°C for refrigerated drugs, can degrade product efficacy. These excursions often occur:
- During warehouse receiving or staging, if cold storage isn’t immediate
- In last-mile delivery when passive cooling solutions fail
- When backup systems malfunction during power outages
The World Health Organization estimates that up to 50% of global vaccines are wasted due to cold chain failures, particularly in the final stages of distribution.
These breakdowns underscore how minor thermal deviations can lead to significant losses and regulatory risk.
B) Contamination Risk from Poor Environmental Controls
In temperature-controlled zones, contamination often stems from:
- Improperly sanitized reusable containers
- Inadequate cleaning protocols for cold rooms
- Condensation and microbial growth due to poor humidity control
A single breach in sterility can result in regulatory action, reprocessing requirements and the loss of entire lots of temperature-sensitive drugs.
C) Noncompliance Due to Improper Storage Infrastructure
Drugs must be stored in validated environments with tight controls over:
- Temperature stability (±0.5°C)
- Humidity (usually 30% to 50% RH for specific products)
- Racking systems that ensure airflow and prevent localized hot spots
Warehouses lacking automated monitoring, real-time alerts or backup power are at constant risk of violating GMP requirements, leading to inspection citations or license suspension.

Process & Data Integrity Risks: Traceability and Recordkeeping
A) Product Loss Due to Improper Chain of Custody
Missing temperature records or poorly documented handoffs make it impossible to verify that a product stayed within safe limits, casting doubt on its integrity.
In such cases, especially with vaccines, the manufacturer typically initiates a recall.
While the FDA rarely mandates recalls directly, it oversees the process to ensure the manufacturer promptly alerts distributors and healthcare providers and follows the proper protocols.
B) Data Integrity and Human Error
Manual, paper-based logs are highly susceptible to human error, falsification, or damage. Under regulations like 21 CFR Part 11, electronic records must be secure, unalterable, and time-stamped.
Without a validated system, data integrity cannot be guaranteed, creating a major compliance vulnerability.
Security & Access Control Risks
A) User Authentication and Access Tracking
In February 2025, Memphis authorities began investigating a theft in which an estimated $250,000 worth of prescription drugs was stolen from a warehouse.
Incidents like this highlight a growing concern: when medications fall into the wrong hands, the consequences extend far beyond financial loss.
Unauthorized access can lead to misuse, patient harm and serious regulatory trouble. Even a single incident can trigger audits, recalls or long-term damage to a company’s reputation.
B) Managing Diverse SKUs
Pharmaceutical warehouses now handle everything from vaccines to injectables and controlled substances, each with its own storage and handling requirements.
Some need ultra-low temperatures, while others demand humidity control or restricted access.
As product variety grows, so does operational complexity. Without flexible warehouse systems, facilities face rising risks of noncompliance, waste and inefficiency.

Best Practices for Managing the Pharmaceutical Cold Storage
Maintaining pharmaceutical compliance in cold chain isn’t just about keeping products cold. It’s about ensuring every process, record, and system supports product integrity and regulatory standards.
Here are some practical best practices to help facilities stay compliant, protect sensitive products, and streamline warehouse operations.
Maintaining a Validated and Resilient Environment
- Monitor Temperatures and Humidity in Real Time
Use calibrated sensors to continuously monitor storage conditions, not just with periodic checks. Real-time data helps detect deviations early and allows your team to act before the product is compromised.
Set automatic alerts to notify staff when thresholds are close to being breached. These controls are essential for maintaining pharma compliance, especially for temperature-sensitive drugs. - Validate and Calibrate Equipment regularly
Cold storage equipment must be revalidated anytime it’s moved, repaired, or upgraded. Routine calibration of all sensors ensures monitoring systems remain accurate and audit-ready.
This includes refrigerators, cold rooms, temperature probes, and alarm systems, all of which must meet pharmaceutical compliance requirements for data integrity and validation. - Plan for Power and Equipment Failures
Poor temperature control doesn’t just lead to product loss; it can also put consumers at serious risk. Cold supply chain management systems help ensure that every item reaching the end user is safe, effective and handled properly.
Executing Compliant Warehouse Procedures
- Keep the Chain of Custody Clear
Document every transfer, whether into storage, between departments or onto a truck, to ensure full traceability. Log who handled the product, when, and under what conditions.
A clear chain of custody not only protects product integrity but also simplifies audits and investigations when needed, both critical to maintaining pharma compliance. - Enforce Strong Hygiene Standards
Even with the right temperature controls, poor hygiene can compromise your cold chain. Clean storage areas regularly, sanitize equipment, and follow strict protocols for reusable containers.
Every surface your product touches should meet validated cleaning standards to prevent contamination and support pharmaceutical compliance across all storage zones. - Use First-Expired, First-Out (FEFO) Inventory Management
Rotate stock based on expiration dates, not simply by arrival order. A warehouse management system (WMS) can automate this process by guiding staff to pick products nearing expiration first, minimizing waste and preserving product quality.
In addition, conduct routine checks for packaging damage and expired inventory to maintain safety and ensure pharmaceutical compliance with inventory control protocols. - Always Wear the Right PPE
Personal protective equipment, like gloves, lab coats, and eye protection, not only safeguards staff but also prevents product contamination.
Ensure employees are properly trained and equipped when handling sensitive or sterile items. For example, vaccines may require insulated gloves, while sterile injectables often demand full gowns and face shields. Consistent PPE use is essential to pharma compliance.

How Modula Automation Supports Pharmaceutical Compliance
To meet the stringent requirements of the pharmaceutical industry, standard storage is insufficient.
Modula warehouse automation offers a line of specialized solutions purpose-built to address the core pillars of pharma compliance.
Modula’s automated storage systems meet FDA and GMP standards with continuous temperature monitoring, RFID-secured access and automated audit-ready reporting.
For Environmental Control: Modula Climate Control
Part of the Modula cold storage lineup, Modula Climate Control is a climate-regulated vertical lift module (VLM) engineered to support cold chain logistics by maintaining stable storage conditions.
It can keep internal temperatures between 36°F and 77°F (2°C to 25°C ±1°C) and relative humidity below 5%, protecting temperature-sensitive drugs from degradation.
By preserving environmental consistency, this solution supports compliance with GDP and GMP requirements for pharmaceutical storage.

Stay on top of temperature and humidity levels.

For Contamination Control: Modula Clean Room
Modula Clean Room is built specifically for use in ISO 14644 Class 7 and 8 cleanroom environments.
This system minimizes the generation and transfer of particulates during operation, making it an essential component for storing sterile instruments, medications, and other sensitive items without risk of contamination.
It supports cleanroom compliance by maintaining hygienic airflow and protecting the storage chamber from particle infiltration.
Maintain compliance with cleanroom standards.

Data Integrity and Access Control With Modula WMS
Data integrity is central to pharmaceutical compliance. A warehouse management system provides the digital backbone for traceability and security.
21 CFR Part 11 support
Modula WMS creates secure, time-stamped electronic records and supports electronic signatures. When configured and validated within your quality system, it helps meet Part 11 expectations for audit trails and record controls.
Complete traceability
Every movement is logged by user, time, lot, and location. The system builds a full chain of custody that simplifies audits and investigations.
Access control
Role-based permissions restrict who can view, pick, or release items. You can limit access at tray or compartment level for controlled or high-value products.
Inventory accuracy and FEFO
The WMS enforces FEFO, guides picks to the correct lot, and reduces manual errors. It also records exceptions and corrective actions.
Environmental and alarm data
Integrate temperature and humidity data with item records. Link alarms to workflows so teams act before a deviation becomes a compliance issue.

When it comes to pharmaceutical compliance, data integrity is everything.

Pharma Compliance Explained: Key Takeaways
Staying compliant in pharmaceutical logistics requires more than just monitoring, as it demands precision, traceability and validated systems.
Modula’s solutions are purpose-built to help you meet these stringent requirements.
- Regulatory agencies like the FDA and GMP guidelines expect tight control over temperature, humidity, traceability and access at every point in the supply chain
- Even small issues, like a brief temperature spike, poor hygiene or missing transfer records, can put product safety at risk and lead to expensive recalls
- Modula’s cold storage solutions, including Modula Climate Control and Modula Clean Room, are built to meet strict standards for GDP, GMP and cleanroom compliance
Speak to our experts and discover how Modula can help you maintain end-to-end compliance.

Protect your pharma supply chain with cold storage solutions.

Pharmaceutical Compliance: FAQs
What is cold chain logistics?
Cold chain logistics refers to the transportation, storage, and handling of temperature-sensitive products through a supply chain that maintains controlled temperature conditions from origin to destination.
What is a pharmaceutical cold chain?
A pharmaceutical cold chain is a temperature-controlled system that protects drug safety and efficacy during packaging, transportation and storage.
This process involves more than refrigeration, as it requires continuous monitoring, secure handling and a documented chain of custody to ensure product integrity from manufacturer to end user.
What is compliance in pharmaceuticals?
Pharma compliance means adhering to the strict regulations (like FDA cGMP) and standards (think USP) that govern how drugs are manufactured, stored, and distributed.
These rules exist to ensure every product is safe, effective, and of consistently high quality.
What is the purpose of cold storage in pharma?
The primary purpose is to protect the chemical and biological integrity of temperature-sensitive drugs, vaccines, and other medical products.
By preventing degradation, cold storage ensures that products remain safe and effective from the point of production until they reach the patient.







